How to Choose a Right Fiber Optic Splitter?
In today's optical network topologies, the advent of fiber optic splitter is significant in helping users maximize the performance of optical network circuits. Fiber optic splitter, or sometimes called as beam splitter, is a passive optical component that can split an incident light beam into two or more light beams, and vice versa. The device contains multiple input and output ends. Whenever the light transmission in a network needs to be divided, fiber optic splitter can be implemented for the convenience of network interconnections.
Fiber Optic Splitter Overview
A fiber optic splitter is a device that splits the fiber optic lights into several parts by a certain ratio. For example, when a beam of fiber optic light transmitted from a 1X4 equal ratio splitter, it will be divided into 4-fiber optic light by equal ratio that is each beam is 1/4 or 25% of the original source one. A fiber optic splitter is different from WDM. WDM can divide the different wavelength fiber optic light into different channels. Fiber optic splitter divides the light power and sends it to different channels. From a technology standpoint, there are two commonly used types of optical splitters: FBT (Fused Biconical Taper) and PLC (Planar Lightwave Circuit).
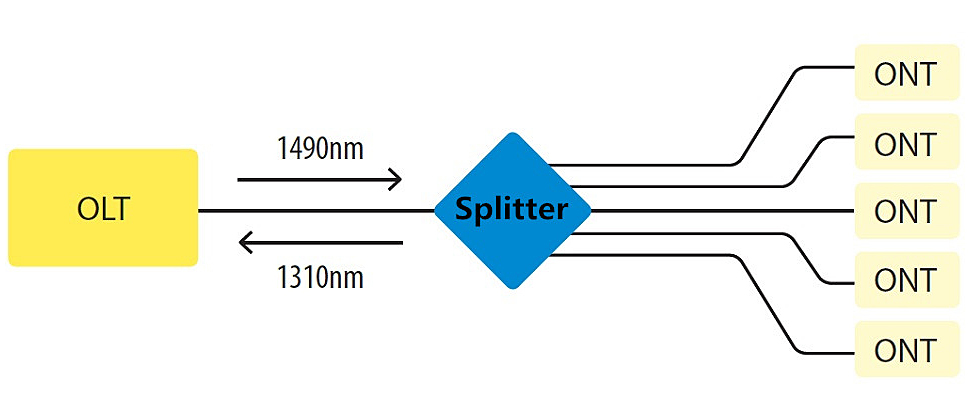
How Does Fiber Optic Splitter Work?
Fiber optic splitter is a key optical device in passive optical network (PON) systems, also known as passive optical splitter. As for the working principle of fiber optic splitter, it can be generally described in the following way. When the light signal transmits in a single-mode fiber, the light energy can not entirely concentrated in the fiber core. A small amount of energy will be spread through the cladding of fiber. That is to say, if two fibers are close enough to each other, the transmitting light in an optical fiber can enter into another optical fiber. Therefore, the reallocation technique of optical signal can be achieved in multiple fibers. And this is how fiber optic splitter comes into being.
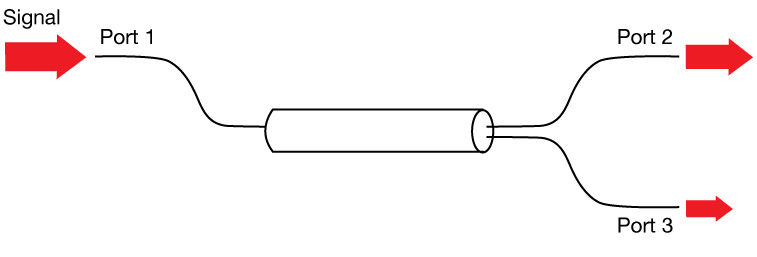
PLC Splitter vs FBT Splitter: What's the Difference?
Splitter technology has forged ahead in the past few years by introducing PLC splitter. It turned out to be a more reliable type of device compared to the traditional FBT splitter. Similarly, both of them are alike in size and outer appearance, and both types of splitters provide data and video access for business and private customers. However, internally the technologies behind these splitters vary, thus giving service providers a possibility to choose a more appropriate solution.
Splitting Ratio Principle
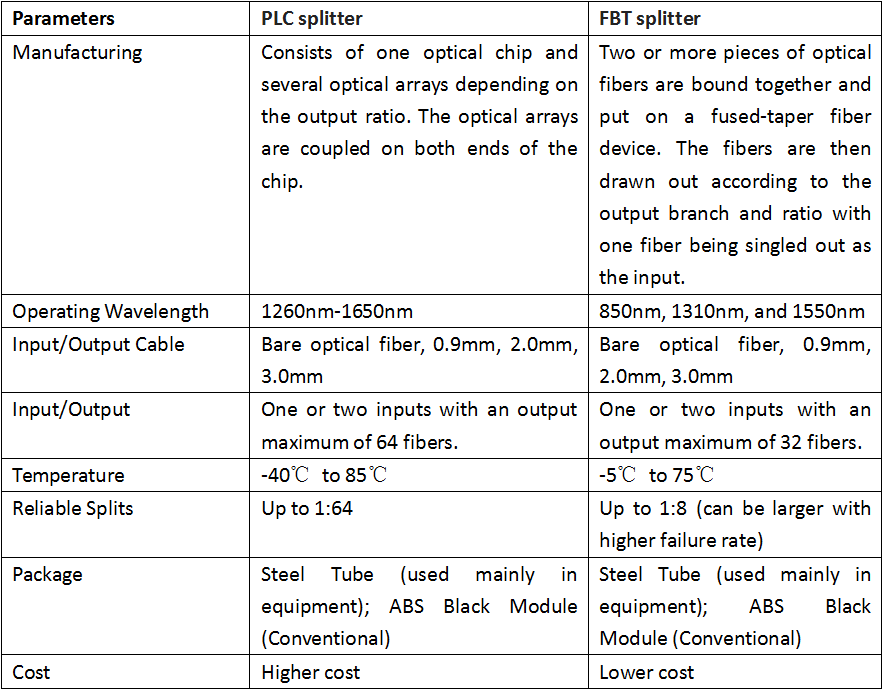
The FBT splitter uses two (or more) fibers. The fibers' coating layer is removed. Both fibers, at the same time, are stretched under a heating zone thus forming a double cone. This special waveguide structure allows control of the splitting ratio via controlling length of the fiber torsion angle and stretch.
The PLC splitter is a micro-optical element using photolithographic techniques to form optical waveguide at medium or semiconductor substrate for realizing branch distribution function.
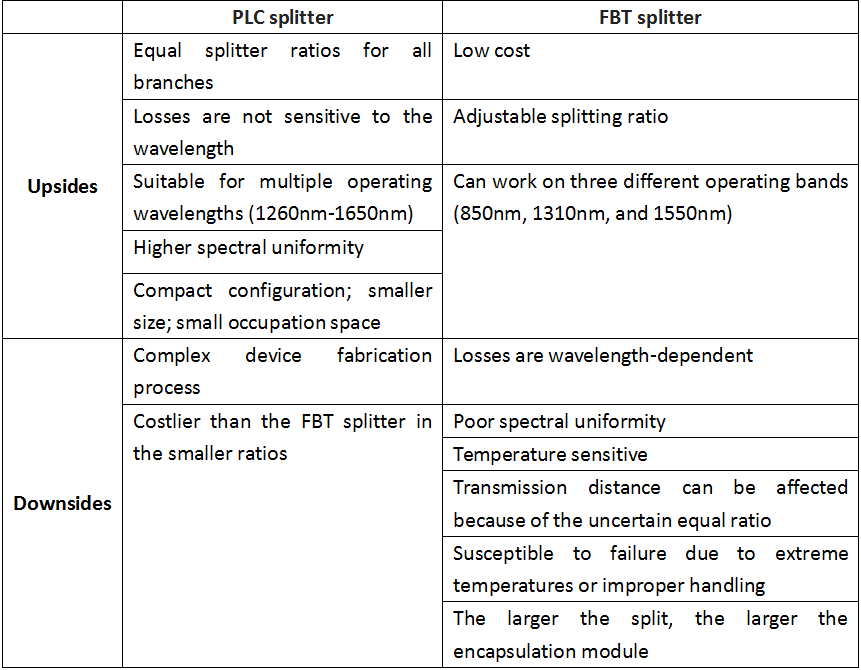
Upsides and Downsides
Optical Performance
How to Choose the Right Fiber Optic Splitter?
In the previous text, we've discussed the difference between FBT and PLC splitters. If you are still confused about which one is the better option for your network, you may find the answer in this part.
Variable and unbalanced optical ratio is the most outstanding advantage of FBT splitter. Sometimes, considering the quantity of user and different transmitting distance, the fiber optical splitter should be adopted for the distribution of optical power in the line. Since the PLC splitter cannot afford the different optical ratio, it is the time to adopt the FBT splitter.
However, comparing with FBT splitter, PLC splitter has the advantages in some other important aspects. Insensitive at different wavelengths, so PLC splitter can work at different wavelength and won't cause much loss. Single component can be split in many channels, reaching 64 or more. And PLC splitter has lower cost for multichannel. The more the channels are, the lower the cost is.
Considering the cost, split configurations below 1×4 are advised to use FBT splitter, while split configurations above 1×8 are recommended for PLC splitters. If only for a single wavelength transmission or dual, FBT splitter is better for save cost. If for PON broadband transmission, considering the future expansion and monitoring needs, PLC splitter is better.
Conclusion
As a leading supplier in fiber optic communication industry, FS.COM provides various kinds of PLC splitters and FBT splitters. Moreover, our fiber optic splitter quality and performance is not only guaranteed by using high-quality components and stringent manufacturing processes and equipment, but also by adherence to a successful quality assurance program. For more details, you can visit www.fs.com.